-40%
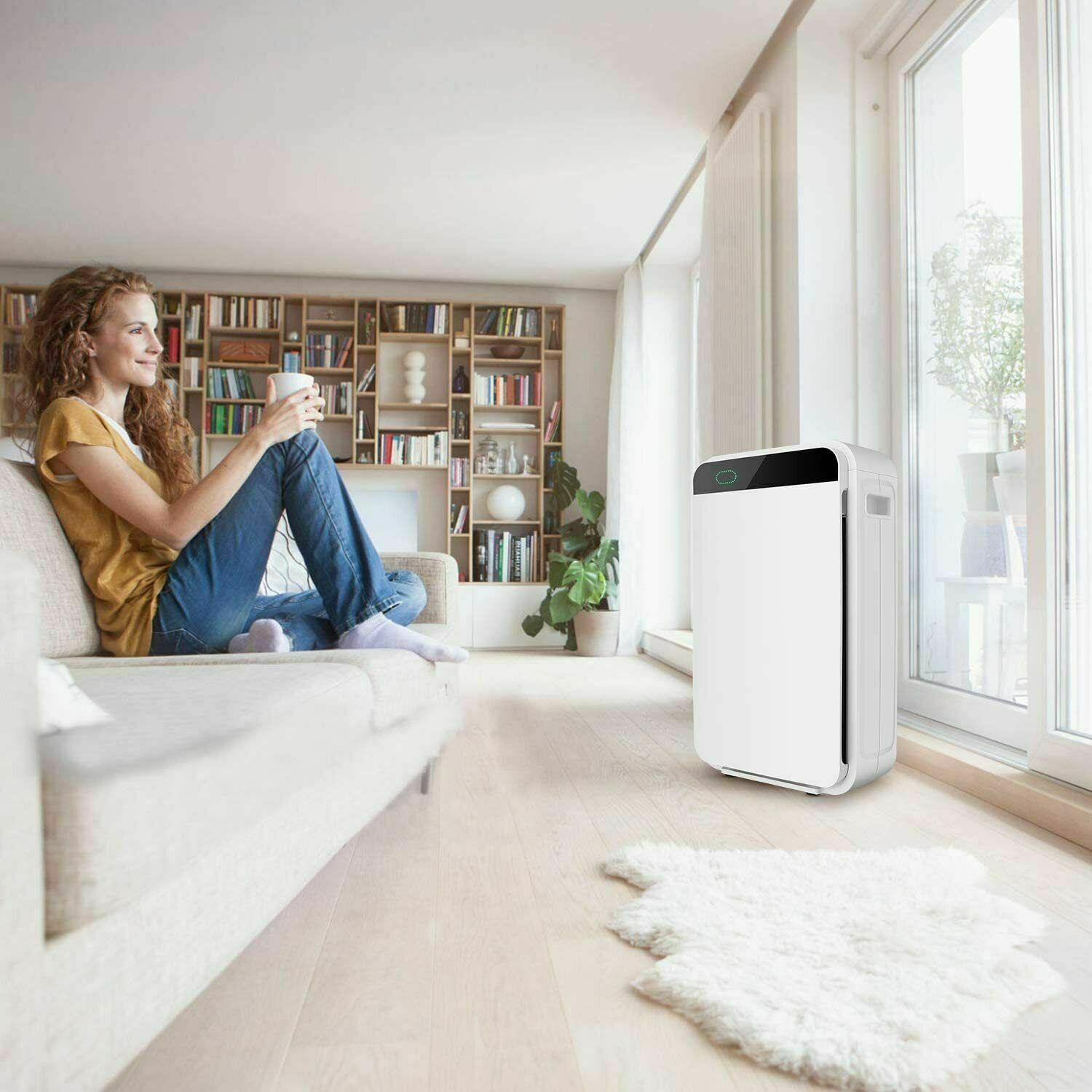
And a Dirty little secret about Air Purification for Asthma, COPD or Virus
$ 157.86
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Filters do not purify the air; they simply capture Germs, Virus and Pathogens in one place.
Left to their own devices, they build colonies.
Lots and lots of deadly colonies.
You don’t change filters because they are dirty;
you change filters because they are loaded with some really nasty
germs that are just sitting there waiting to escape back into the atmosphere.
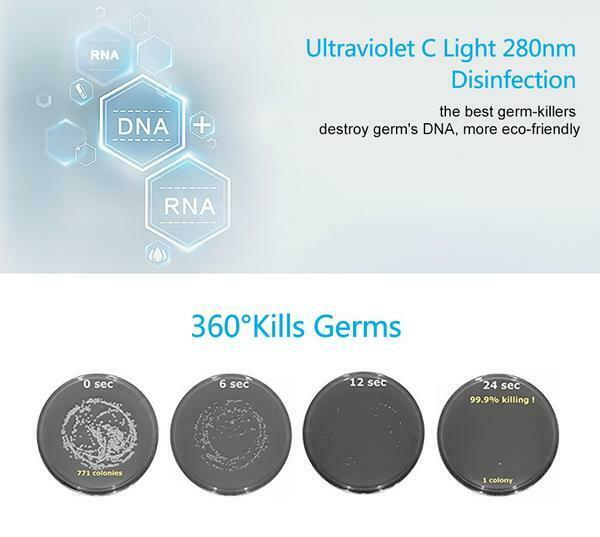
The answer is what Hospitals, Scientific Labs and Clean rooms utilize.
It is called Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation or UVGI for short.
You sterilize the filters the second the germs are captured.
You do this by having a UV-C light at 254.7nm inside a crystal blown glass casing.
Not cheap, but very effective.
That is why we guarantee our light bulbs forever with a Lifetime Guarantee.
Simply mail back the old bulb; we will mail you a new one.
Don’t hold your breath as we have had one burning for three years and it is still going strong at 99% effective.
Air Purifiers and Remediation
Why does commercial air purifiers in Hospitals, Nursing Homes and Clean Rooms in Biological Research Laboratories cost over a Thousand Dollars?
Is an inexpensive home unit bought at Wal-Mart® for .99 just as effective in cleaning the air as a 00 medical unit? Does it clean the air ten times better if you spend more?
If you asked a Hospital or Research lab what the absolute best sterilization method known to medical science, they would tell you it is not just one single method, but a combination of the all of the medical breakthroughs coupled with modern science and the latest technological advances in electronics.
A hospital bed is no longer just a bed, it is a computer.
The best is not just one single item, but a cocktail of all the known protocols for medical advancement.
It started in 1903 when Niels Finsen was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in coming up with a cure for tuberculosis using a Ultraviolet light at precisely 254.7nm which is a germicide. You don’t hear much about TB anymore because UV light eradicated the deadly disease.
Then came the second world war and the HEPA filter was designed in the 1940s and was used in the Manhattan Project to prevent the spread of airborne radioactive contaminants. The US Army Chemical Corps and National Defense Research Committee needed to develop a filter suitable for removing radioactive materials from the air. The Army Chemical Corps asked Nobel Laureate Irving Langmuir to recommend filter test methods and other general recommendations for creating the material to filter out these radioactive particles. He identified 0.3 micron size particles to be the "most penetrating size" - the most difficult and concerning.
Do you see a pattern emerging and it has to do with Nobel Laureates coming up with scientific breakthroughs and thinking outside of the box.
Then came Steve Jobs and his little computer. Let’s now forget Bill Gates and his traffic cop program that directed the ebb and flow of some pretty remarkable and some would call genius inventions.
Intel developed a magical little mother board that gave life to an invention that would change the world.
We now live longer because someone thought of it, they believe it and look where we are because of it.
You want to live to be a Hundred?
Want a cure for Lung Cancer?
What if we got rid of the common cold by utilizing Science and Technology?
Read on, we are on the very cusp of the greatest invention ever discovered.
Biomedical
HEPA filters are critical in the prevention of the spread of airborne bacterial and viral organisms and, therefore, infection. Typically, medical use HEPA filtration systems also incorporate high-energy
ultra-violet light
units or panels with anti-microbial coating to kill off the live bacteria and
viruses
trapped by the filter media. Some of the best-rated HEPA units have an efficiency rating of 99.995%, which assures a very high level of protection against airborne disease transmission.
A high-quality HEPA filter that can trap 99.97% of dust particles that are 0.3 microns in diameter. For comparisons sake, a human hair is about 50 to 150 microns in diameter. So, a true HEPA filter is effectively trapping particles several hundred times smaller than the width of a human hair. A particle of dust so small that you cannot see it with the human eye and yet a HEPA filter captures it.
HEPA filters are composed of a mat of randomly arranged fibers. The fibers are typically composed of fiberglass and possess diameters between 0.5 and 2.0 micrometers. Key factors affecting its functions are fiber diameter, filter thickness, and face velocity. The air space between HEPA filter fibers is typically much greater than 0.3 μm. The common assumption
[
that a HEPA filter acts like a sieve where particles smaller than the largest opening can pass through is incorrect and impractical. Unlike membrane filters at this pore size, where particles as wide as the largest opening or distance between fibers cannot pass in between them at all, HEPA filters are designed to target much smaller pollutants and particles. These particles are trapped (they stick to a fiber) through a combination of the following three mechanisms:
Diffusion
An enhancing mechanism that is a result of the collision with gas molecules by the smallest particles, especially those below 0.1 μm in diameter, which are thereby impeded and delayed in their path through the filter; this behavior is similar to Brownian motion and raises the probability that a particle will be stopped by either interception or impaction; this mechanism becomes dominant at lower air flow.
Interception
Particles following a line of flow in the air stream come within one radius of a fiber and adhere to it.
Impaction
Larger particles are unable to avoid fibers by following the curving contours of the air stream and are forced to embed in one of them directly; this effect increases with diminishing fiber separation and higher air flow velocity.
Diffusion predominates below the 0.1 μm diameter particle size, whilst impaction and interception predominate above 0.4 μm. In between, near the most penetrating particle size (MPPS) 0.21 μm, both diffusion and interception are comparatively inefficient. Because this is the weakest point in the filter's performance, the HEPA specifications use the retention of particles near this size (0.3 μm) to classify the filter. However it is possible for particles smaller than the MPPS to not have filtering efficiency greater than that of the MPPS. This is due to the fact that these particles can act as nucleation sites for mostly condensation and form particles near the MPPS.
Gas filtration
HEPA filters are designed to arrest very fine particles effectively, but they do not filter out gasses and odor molecules. Circumstances requiring filtration of volatile organic compounds (VOC), chemical vapors, cigarette, pet or flatulence odors call for the use of an activated carbon (charcoal) or other type of filter instead of or in addition to a HEPA filter. Carbon cloth filters, claimed to be many times more efficient than the granular activated carbon form at adsorption of gaseous pollutants, are known as High Efficiency Gas Adsorption filters (HEGA) and were originally developed by the British military as a defense against chemical warfare
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
A HEPA filter can be used in conjunction with a pre-filter (usually carbon-activated) to extend the usage life of the more expensive HEPA filter. In such setup, the first stage in the filtration process is made up of a pre-filter which removes most of the larger dust, hair, PM10 and pollen particles from the air. The second stage high-quality HEPA filter, which filters out the finer particles that escapes from the pre-filter. The coup de gras or the ultimate killer of disease would have to be coupled with a Ultraviolet light at precisely 254.7nm in a hand blown crystal glass casing.
These elements are the part and parcel of any great air purification system.
Without it, you just have a fan blowing air through a cheap filter.
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is used to treat poisonings and overdoses following oral ingestion. Tablets or capsules of activated carbon are used in many countries as an over-the-counter drug to treat diarrhea, indigestion, and flatulence. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the safest and most effective medicines needed in a health system.
It is there for a reason.
Medically, activated carbon removes gases and other harmful bacteria from the air.
Activated Charcoal filters are in important part of an air purifier system in conjunction with other powerful germ, virus and pathogen killers.
An
air purifier
or
air cleaner
is a device which removes contaminants from the air in a room to improve indoor air quality. These devices are commonly marketed as being beneficial to allergy sufferers and asthmatics, and at reducing or eliminating second-hand tobacco smoke.
The commercially graded air purifiers are manufactured as either small stand-alone units or larger units that can be affixed to an air handler unit (AHU) or to an HVAC unit found in the medical, industrial, and commercial industries. Air purifiers may also be used in industry to remove impurities from air before processing.
All this leads us to why we want an air purifier in the first place. The answer is simple.
Indoor Air Quality or IAQ can be the difference of being sick all the time, sick and tired of being sick and tired and downright infectious disease.
Air quality within and around buildings and structures
Indoor air quality
(
IAQ
) is the air quality within and around
buildings
and
structures
. IAQ is known to affect the health, comfort and well-being of building occupants. Poor indoor air quality has been linked to
sick building syndrome
, reduced productivity and impaired learning in schools.
IAQ can be affected by gases (including
carbon monoxide
,
radon
,
volatile organic compounds
),
particulates
,
microbial
contaminants (
mold
,
bacteria
), or any mass or energy stressor that can induce adverse health conditions. Source control, filtration and the use of
ventilation
to dilute contaminants are the primary methods for improving indoor air quality in most buildings. Residential units can further improve indoor air quality by routine cleaning of carpets and area rugs.
Determination of IAQ involves the collection of air samples, monitoring human exposure to pollutants, collection of samples on building surfaces, and computer modelling of air flow inside buildings.
IAQ is part of
indoor environmental quality
(IEQ), which includes IAQ as well as other physical and psychological aspects of life indoors (e.g., lighting, visual quality, acoustics, and thermal comfort).
[1]
Molds and other allergens
These biological chemicals can arise from a host of means, but there are two common classes: (a) moisture induced growth of mold colonies and (b) natural substances released into the air such as animal dander and plant pollen. Mold is always associated with moisture
and its growth can be inhibited by keeping humidity levels below 50%. Moisture buildup inside buildings may arise from water penetrating compromised areas of the building envelope or skin, from plumbing leaks, from
condensation
due to improper ventilation, or from ground moisture penetrating a building part. Even something as simple as drying clothes indoors on
radiators
can increase the risk of exposure to (amongst other things)
Aspergillus
– a highly dangerous mould that can be fatal for asthma sufferers and the elderly. In areas where cellulosic materials (paper and wood, including drywall) become moist and fail to dry within 48 hours, mold mildew can propagate and release allergenic spores into the air.
In many cases, if materials have failed to dry out several days after the suspected water event, mold growth is suspected within wall cavities even if it is not immediately visible. Through a mold investigation, which may include destructive inspection, one should be able to determine the presence or absence of mold. In a situation where there is visible mold and the indoor air quality may have been compromised, mold remediation may be needed. Mold testing and inspections should be carried out by an independent investigator to avoid any conflict of interest and to insure accurate results; free mold testing offered by remediation companies is not recommended.
There are some varieties of mold that contain toxic compounds (mycotoxins). However, exposure to hazardous levels of mycotoxin via inhalation is not possible in most cases, as toxins are produced by the fungal body and are not at significant levels in the released spores. The primary hazard of mold growth, as it relates to indoor air quality, comes from the allergenic properties of the spore cell wall. More serious than most allergenic properties is the ability of mold to trigger episodes in persons that already have
asthma
, a serious respiratory disease.
Volatile organic compounds
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted as gases from certain solids or liquids. VOCs include a variety of chemicals, some of which may have short- and long-term adverse health effects. Concentrations of many VOCs are consistently higher indoors (up to ten times higher) than outdoors. VOCs are emitted by a wide array of products numbering in the thousands. Examples include: paints and lacquers, paint strippers, cleaning supplies, pesticides, building materials and furnishings, office equipment such as copiers and printers, correction fluids and carbonless copy paper, graphics and craft materials including glues and adhesives, permanent markers, and photographic solutions.
Chlorinated drinking water releases chloroform when hot water is used in the home. Benzene is emitted from fuel stored in attached garages. Overheated cooking oils emit acrolein and formaldehyde. A meta-analysis of 77 surveys of VOCs in homes in the US found the top ten riskiest indoor air VOCs were acrolein, formaldehyde, benzene, hexachlorobutadiene, acetaldehyde, 1,3-butadiene, benzyl chloride, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, carbon tetrachloride, acrylonitrile, and vinyl chloride. These compounds exceeded health standards in most homes.
[17]
Organic chemicals are widely used as ingredients in household products. Paints, varnishes, and wax all contain organic solvents, as do many cleaning, disinfecting, cosmetic, degreasing, and hobby products. Fuels are made up of organic chemicals. All of these products can release organic compounds during usage, and, to some degree, when they are stored. Testing emissions from building materials used indoors has become increasingly common for floor coverings, paints, and many other important indoor building materials and finishes.
Several initiatives envisage to reduce indoor air contamination by limiting VOC emissions from products. There are regulations in France and in Germany, and numerous voluntary ecolabels and rating systems containing low VOC emissions criteria such as EMICODE, M1, Blue Angel and Indoor Air Comfort in Europe, as well as California Standard CDPH Section 01350 and several others in the USA. These initiatives changed the marketplace where an increasing number of low-emitting products has become available during the last decades.
Ozone
Ozone is produced by Ozone generators such as SoClean®
Ozone exists in greater concentrations at altitudes commonly flown by passenger jets. Reactions between ozone and onboard substances, including skin oils and cosmetics, can produce toxic chemicals as by-products. Ozone itself is also irritating to lung tissue and harmful to human health. Larger jets have ozone filters to reduce the cabin concentration to safer and more comfortable levels.
Outdoor air used for ventilation may have sufficient ozone to react with common indoor pollutants as well as skin oils and other common indoor air chemicals or surfaces. Particular concern is warranted when using "green" cleaning products based on citrus or terpene extracts, because these chemicals react very quickly with ozone to form toxic and irritating chemicals as well as fine and ultrafine particles. Ventilation with outdoor air containing elevated ozone concentrations may complicate remediation attempts.
Ozone is on the list of six criteria air pollutant list. The Clean Air Act of 1990 required the United States Environmental Protection Agency to set National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for six common indoor air pollutants harmful to human health.
[34]
There are also multiple other organizations that have put forth air standards such as Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), and the World Health Organization (WHO). The OSHA standard for Ozone concentration within a space is 0.1 ppm. While the NAAQS and the EPA standard for ozone concentration is limited to 0.07 ppm. The type of ozone being regulated is ground-level ozone that is within the breathing range of most building occupants
Legionella
Legionellosis or Legionnaire's Disease is caused by a waterborne bacterium
Legionella
that grows best in slow-moving or still, warm water. The primary route of exposure is through the creation of an aerosol effect, most commonly from evaporative cooling towers or showerheads. A common source of Legionella in commercial buildings is from poorly placed or maintained evaporative cooling towers, which often release water in an aerosol which may enter nearby ventilation intakes. Outbreaks in medical facilities and nursing homes, where patients are immuno-suppressed and immuno-weak, are the most commonly reported cases of Legionellosis. More than one case has involved outdoor fountains in public attractions. The presence of Legionella in commercial building water supplies is highly under-reported, as healthy people require heavy exposure to acquire infection.
Legionella testing typically involves collecting water samples and surface swabs from evaporative cooling basins, shower heads, faucets/taps, and other locations where warm water collects. The samples are then cultured and colony forming units (cfu) of Legionella are quantified as cfu/Liter.
Legionella is a parasite of protozoan such as
amoeba
, and thus requires conditions suitable for both organisms. The bacterium forms a
biofilm
which is resistant to chemical and antimicrobial treatments, including chlorine. Remediation for Legionella outbreaks in commercial buildings vary, but often include very hot water flushes (160 °F; 70 °C), sterilization of standing water in evaporative cooling basins, replacement of shower heads, and in some cases flushes of heavy metal salts. Preventive measures include adjusting normal hot water levels to allow for 120 °F (50 °C) at the tap, evaluating facility design layout, removing faucet aerators, and periodic testing in suspect areas.
Building ecology
It is common to assume that buildings are simply inanimate physical entities, relatively stable over time. This implies that there is little interaction between the triad of the building, what is in it (occupants and contents), and what is around it (the larger environment). We commonly see the overwhelming majority of the mass of material in a building as relatively unchanged physical material over time. In fact, the true nature of buildings can be viewed as the result of a complex set of dynamic interactions among their physical, chemical, and biological dimensions. Buildings can be described and understood as complex systems. Research applying the approaches ecologists use to the understanding of ecosystems can help increase our understanding. “Building ecology “ is proposed here as the application of those approaches to the built environment considering the dynamic system of buildings, their occupants, and the larger environment.
Buildings constantly evolve as a result of the changes in the environment around them as well as the occupants, materials, and activities within them. The various surfaces and the air inside a building are constantly interacting, and this interaction results in changes in each. For example, we may see a window as changing slightly over time as it becomes dirty, then is cleaned, accumulates dirt again, is cleaned again, and so on through its life. In fact, the “dirt” we see may be evolving as a result of the interactions among the moisture, chemicals, and biological materials found there.
Buildings are designed or intended to respond actively to some of these changes in and around them with heating, cooling, ventilating, air cleaning or illuminating systems. We clean, sanitize, and maintain surfaces to enhance their appearance, performance, or longevity. In other cases, such changes subtly or even dramatically alter buildings in ways that may be important to their own integrity or their impact on building occupants through the evolution of the physical, chemical, and biological processes that define them at any time. We may find it useful to combine the tools of the physical sciences with those of the biological sciences and, especially, some of the approaches used by scientists studying ecosystems, in order to gain an enhanced understanding of the environments in which we spend the majority of our time, our buildings.
Now let’s look at what years of Government research says about air purifiers.
First, the flavor of the month a few years back was OZONE.
Air purifiers and Cpap cleaners like SoClean® were nothing more than Ozone Generators and yet disguised themselves as pure air.
Ozone Generators that are Sold as Air Cleaners
There is a large body of written material on ozone and the use of ozone indoors. However, much of this material makes claims or draws conclusions without substantiation and sound science. In developing
Ozone Generators that are Sold as Air Cleaners
, the EPA reviewed a wide assortment of this literature, including information provided by a leading manufacturer of ozone generating devices. In keeping with EPA's policy of insuring that the information it provides is based on sound science, only peer reviewed, scientifically supported findings and conclusions were relied upon in developing this document.
The bottom line on ozone is use with caution. It could kill you on a worst case scenario and make you deathly ill on the very best case.
According to research studies conducted by the Center for Disease Control, they recommend you do not use an air purifier system with ozone.
Use something else. It is safer!
Now if you have read this far, you probably deserve a Doctorate Degree from MIT.
By now, you understand that a fan and filter just isn’t what you need for an air purification system.
NASA discovered this when they realized there is no “do over” if astronauts run out of clean air in outer space.
Same is true here on earth.
Here is the basics you need;
1).
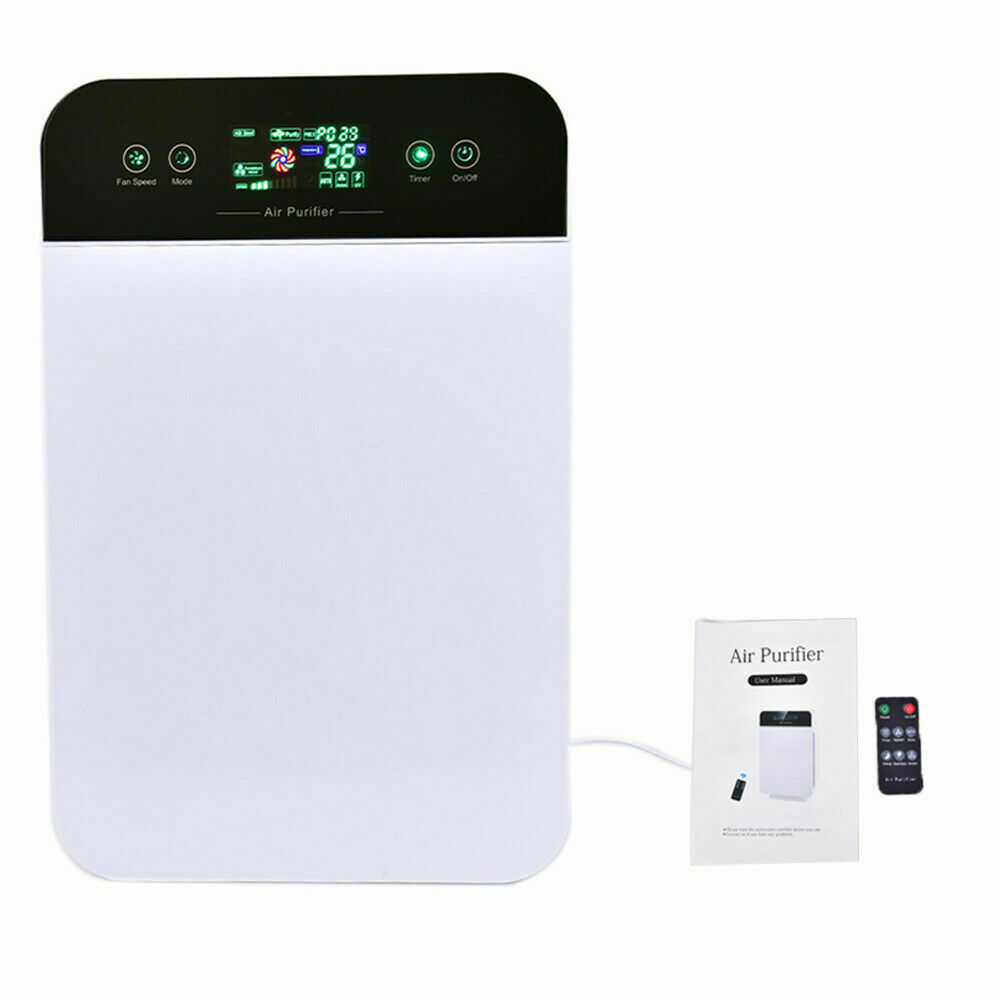
A computer panel that lights up like the space shuttle would be nice.
Computers direct the ebb and flow of things.
It should at the very least show the ambient temperature, the speed of the fan, the air quality in easy to understand color coding that Green is good, Blue is acceptable and the unit is working on it to make things better and Red you better get out of Dodge.
A built in timer to set the amount of hours it will run to conserve the filters.
Twenty four hour a day usage will wear out the filters in ninety days whereas using it from one to Eight hours will extend the life of very expensive filters.
A sleep mode would be useful to keep the unit from rocking our eye teeth out at night time when things should be quiet.
A built in fail safe back up system in case the Department of
Health issues Health advisory.
An
Air Quality Health Advisory
is a graphic email/text notification which tells the subscriber
air pollution
levels are currently unhealthy for sensitive groups
.
This back up system is usually manually turned on when things turn to crap.
Normally, it is an electronic ion field. It is usually used for Cigar Smoke, Smog and Cigarette use. A light should indicate when it is on. It would also be nice to have a digital display showing the fan turning over slow, medium or high.
Graphics are nice.
2)
Without a Germicidal light to kill virus, bacteria, germs and pathogens, you have no air purification system, only a fan and a filter. One should realize that filters are there to capture dead cells and micro organisms that Ultraviolet light kills.
Think of it as the car engine.
You need a filter to clean out all the dirty stuff going through the oil, but without the spark plugs lighting the place up like the fourth of July, you have no power.
Same is true with UV germicidal light.
You need something to kill all that bacteria and virus before it can spread and multiply.
I am always amazed at some companies that put an LED Blue light in and call it germicidal.
These things are night lights and serve no useful purpose in killing germs and virus. If it doesn’t say 254.7nm, you don’t have a germicide.
You have a pretty little ligth but not a death ray for bad stuff that can infect you and your family.
3)
You need a bunch of filters.
The first of course is a prefilter usually covering up the HEPA filter to keep creepy crawly things from wondering in.
4)
The grand daddy of them all is a HEPA filter and it isn’t cheap.
Now you can buy cheap ones that are used for a vacuum cleaner or put into the ductwork of your A/C or Heat system but these are rated at about 5 and are about as effective as putting a band-aid on a heart transplant.
Not very effective.
MERV ratings range from 1 to 20, with 1 being the lowest level of filtration, and 20 being the highest. Filters that are MERV 16 through 20 are usually only found in hospitals, cleanrooms, and nuclear power plants. The home air filters you're looking for are rated anywhere between MERV 5 and 13
MERV stands for Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value, which is a rating system designed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE)
5).
Now we get into some really interesting filters that separate the men from the boys.
The HEPA and the Charcoal filters are the reason that Wal-Mart sells a hundred dollar fan and filter and the Swiss (who make ,000 Rolex watches) charge a Thousand Dollars for a really good air purification system.
Carbon air filters remove pollutants from the air with a process known as adsorption. Note that this is different from absorption. In absorption, the substance you want to remove (let’s say water) is absorbed into the structure of the absorbent (like a sponge), but it doesn’t become a part of the absorbent on a molecular level. Therefore, when you absorb water with a sponge, the water does not become chemically bonded to the sponge. It just fills in the spaces inside it.
Carbon is a lattice of carbon atoms connected to each other. The activation process is so important because the increase in surface area gives gases a greater area to stick to. When a molecule of some gaseous substance comes through the carbon, it can stick to the surface of the bed, provided there is an open adsorption site.
Air flow is vital.
To remove the most pollutants possible from the air, the air needs to spend the maximum possible amount of time passing through the carbon. In the air filter industry, this is known as “dwell time.” A filter with a good amount of carbon of sufficient thickness and high dwell time is going to be far more effective than a filter with a thin layer of carbon.
There is the answer.
You read all this way to come to a very simple conclusion.
It is what is inside these things that cost a bundle, not the hype of advertising that tells you it is cleaning something you cannot see with the naked eye.
First off, they use LED lights because they can mass produce them for a few cents.
Genuine Ultraviolet Germicidal lights are at precisely 254.7nm and are made of hand blown glass.
Think about that for a second and where would you go to get hand blown glass.
The reason is in science.
UV light will not pass through normal window glass, car glass or even plastic.
So you can’t make it cheap.
It will only pass through silicone (that’s another story) and hand blown Crystal Glass.
Hidden out of sight in a UV light fixture is what is called a ballast that controls and reduces the amount of energy it takes to fire one of these things up.
It is a computer folks, and it also has a mother board.
Try and build one of those cheap.
Then comes the filtering system.
Very cheap HEPA filters might be good for warehouse but not for a nuclear power plant, a hospital operating theatre or a nursing home that has hightly susceptible occupants to flu.
You want the best or people die.
Same is true with carbon filers that were developed by the Military to fight chemical warfare agents.
So there you have it. That is the dirty little secret that no one wants you to know.
Air purification is a science.
Quality comes with a price tag.
My product should sell for over a thousand dollars per unit, but I sell it on eBay for 9.
If you were smart, you would buy one and sell it to the Swiss for a Thousand Dollars. My unit is better.